Project 6 - Space Partitioning
Tracing rays through triangular meshes has been drastically sped up due to partitioning space with bounding volume hierarchy (BVH) structures. This ensures that the ray-triangle intersection code is only being called for rays nearly hitting those triangles, rather than calling this function for all triangles every time a ray hits the object’s bounding box. It is interesting to note that the bounding boxes we used last project actually slow down the BVH structures, since we are essentially using a computation twice (checking the root node of the BVH and also the bounding box for the object). Lastly, computation times are shown for our box scene using two different ray-triangle intersection algorithms: the 2D area-based algorithm described in class and the Moller-Trumbore algorithm.
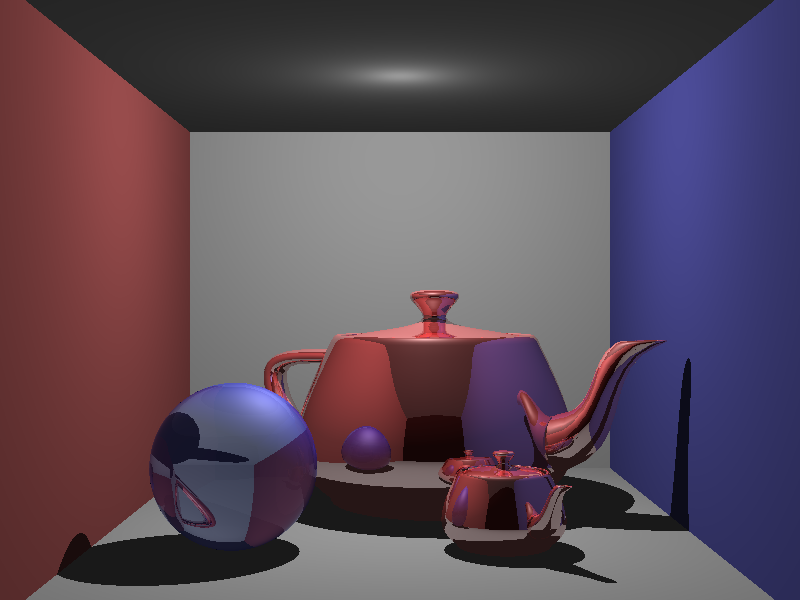
Box Scene (with teapot)
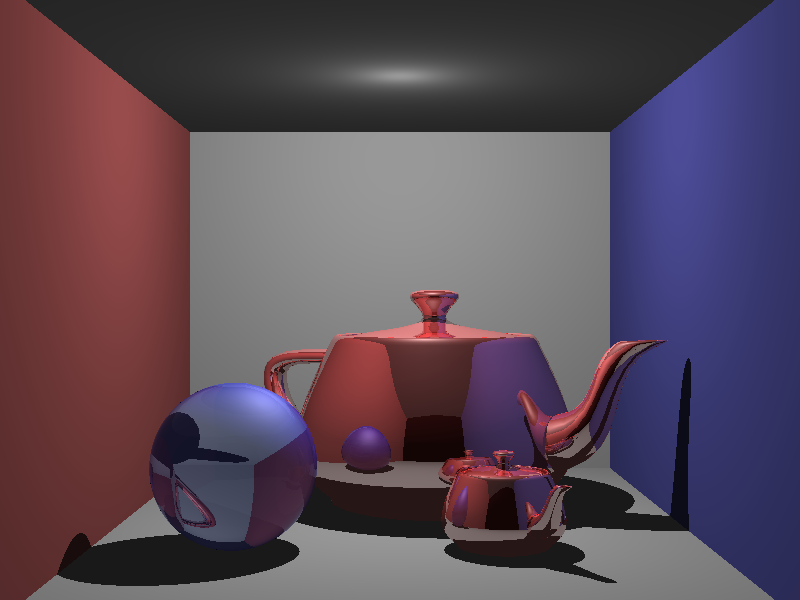
Box Scene (area–2D intersection)
Comparing Algorithms
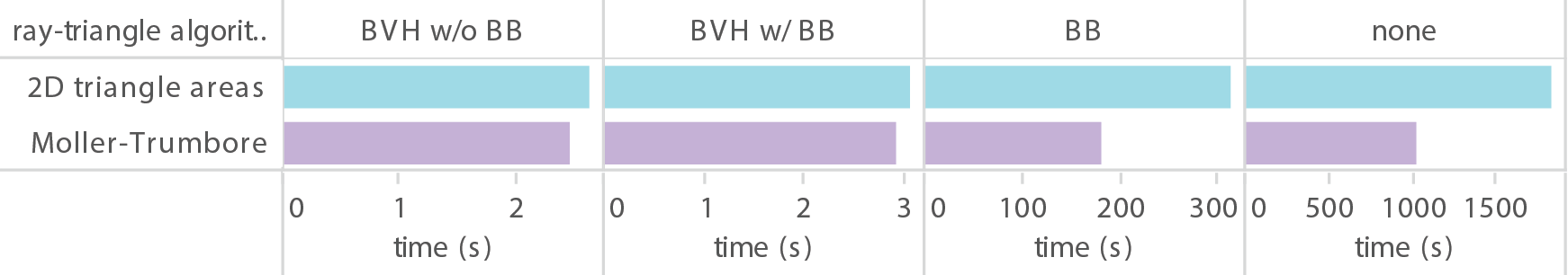
Details
| ray-triangle algorithm | BVH w/o BB | BVH w/ BB | BB | none |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D triangle areas | 2.631 s | 3.055 s | 5 min 11.704 s | 30 m 20.151 s |
| Moller-Trumbore | 2.478 s | 2.919 s | 3 min 00.762 s | 17 m 01.971 s |